

Modular-mobile water treatment system (2017)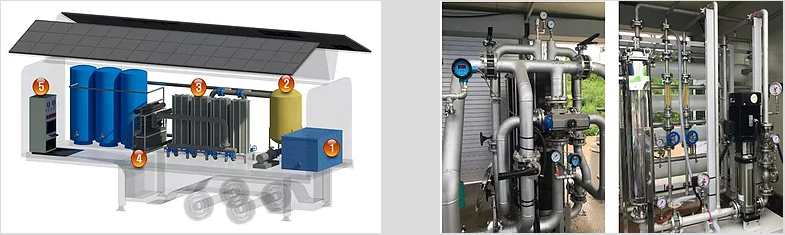
It is necessary to develop a mobile water production system in order to provide stable water supply in case of disasters such as floods or earthquakes. In this study, we developed a modular mobile water production system capable of producing water for various uses such as domestic water and drinking water while improving applicability in various raw water sources. The water production system consists of three stages of filtration (sand filtration - activated carbon filtration - pressure filtration) to produce domestic water and an additional reverse osmosis process to produce drinking water. The mobile water production system developed in this study is expected to be used not only in water supply in case of disaster, but also wildly used in islands and rural area.
Nano-composite materials for selective adsorption of heavy metal (Cd) (2015-2017)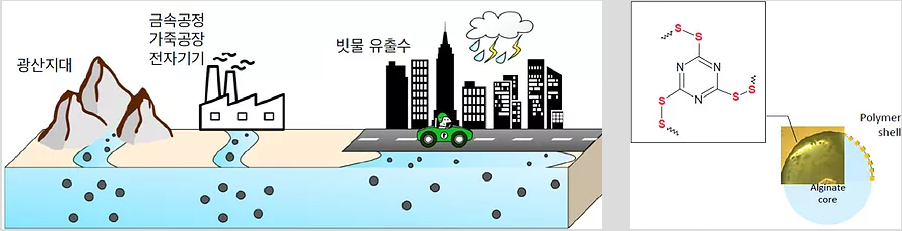
Contamination by heavy metal ions, such as cadmium, lead, copper, and zinc, has been a persistent problem to the environment and humans for several millennia, and yet considerable amounts of heavy metals still originate from industrial operations, for example mining, stormwater runoff and even agriculture. The demand for new adsorbents, which not only have a high surface area, but also are selective, continues to drive research into efficient and functionalized sorbent materials. We are studying to develop nanomaterials having specific affinity towards desired heavy metal ions to be used as water treatment operation. However, nanomaterials are not considered to be practical materials for water treatment due to its small size. We are trying to make nano-composite materials to be used as water treatment column or filtration system, which can provide practical applicability for nanomaterials while nano effect can be expected. Currently, surfur based organic polymer for cadmium adsorption and prussian blue based composite materials for cesium uptake are studying.
Sensing techniques for determining redox reactivity of nanomaterials (2014-2016)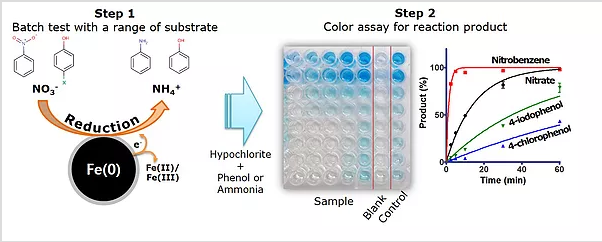
We adapted colorimetric assays for determining reductive activity of nZVI and its composites with other metals. The assay quantifies reduction products to avoid interfering reactions, such as sorption and volatilization. Three different reaction products, ammonium, phenol, and aniline, generated as the result of reduction of nitrate, p-halophenols, and nitrobenzene, respectively, could be quantified using the same reagent for all reactions. The colorimetric assays were further adapted to the 96-well microplate format, thus minimizing sample and reagent use, as well as lowering color development time to 2 h. The substrates showed graduated reactivity and thus reduction potency and kinetics of different materials and reaction mechanism was distinguished. The applicability was successfully proven by determining the reactivity of a commercial nZVI sample, and investigating the effect of nickel content on dehalogenation. Therefore, the suggested reactivity test with different compounds, combined with the use of a multi-well microplate based color assay, promises to be a useful and simple tool in various nZVI related research topics.
Filtration system for non-point pollution control (2016)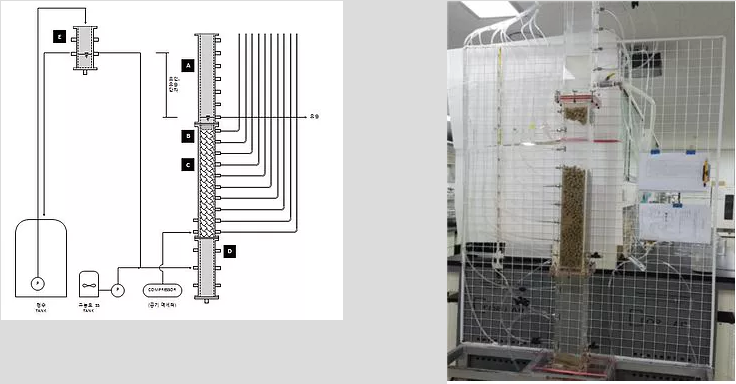
Since many small facilities are installed on the roadside for controlling non-point source pollution, it is necessary to establish optimal conditions to minimize maintenance cost. In this study, an upflow filtration system consisting of the lower settling tank and the upper filtration unit was constructed using a ceramic filter media and floating filter media. More than 96% of suspended solid could be removed. Especially, it was confirmed that suspended solids having a certain particle size can be effectively removed at lower settling tank, which can minimize a load to the upper filtration unit. In order to establish optimal backwashing conditions, the effects of time and flow rate of air and water, and the presence of stagnant water discharge process were investigated. It was found that the introduction of the stagnant water discharge process between air washing and water washing processes should be considered in order to minimize the release of suspended solids immediately after backwashing.